「Moving Average Filter」の版間の差分
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
== | ==Ideal Model (理想モデル) == | ||
=== Representation in frequency domain (周波数軸での表記)=== | === Representation in frequency domain (周波数軸での表記)=== | ||
2016年12月25日 (日) 11:21時点における版
Ideal Model (理想モデル)
Representation in frequency domain (周波数軸での表記)
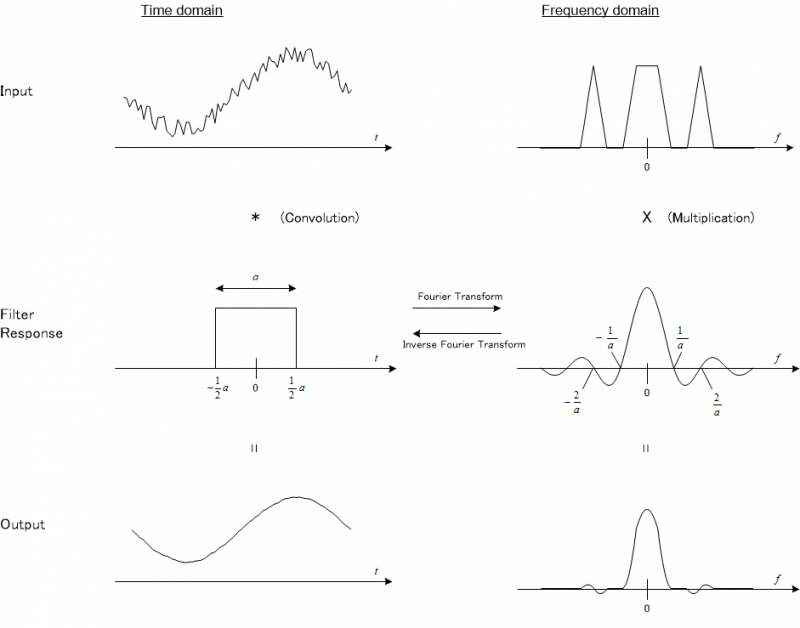
Moving Average Filter performs convolution of input signal and rectangular pulse in time domain.
The convolution in time domain equals point-wise multiplication in frequency domain. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convolution_theorem)
Thus the frequency response of Moving Average Filter is a representation of rectangular pulse in frequency domain, and obtained by performing Fourier Transform of the rectangular pulse. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rectangular_function)
Note that the frequency response here is a complex representation but all imaginary components are zero.
移動平均フィルタでは、時間軸において、入力信号と矩形パルスの畳み込み積分が行われます。
畳み込み積分は周波数軸において、周波数成分ごとの乗算と等価となります。
従って、移動平均フィルタの周波数特性は、矩形パルスの周波数軸での表記として表され、矩形パルスをフーリエ変換することで求めることができます。
なお、ここでの周波数特性は複素表記ですが、虚数部は全てゼロになります。
Frequency response in dB (周波数特性のdB換算)
Frequency response of Moving Average Filter in dB is shown as the following.
移動平均フィルタの周波数特性をdB表記すると、以下のようになります。
Example (例)
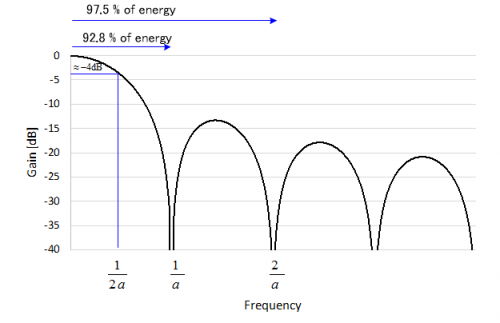
Suppose sampling frequency is 1[kHz] and averaging over 10 samples, we use a=10[ms].
We can observe the 92.8% of the power spectrum from this filter is below 100 [Hz], if the input is an impulse.
If we resample this filter output at 200[Hz], a distortion of 7.2% is expected due to aliasing error happens over 100[Hz] components.
1[kHz]でサンプリングを行い、10個のサンプルを平均化する場合、a=10[ms]となります。
上の図より、インパルス入力の場合、フィルタの出力の92.8%の電力スペクトラムは100[Hz]以内に入ることが分かります。
このフィルタの出力を200[Hz]で再サンプリングを行った場合、100[Hz]以上の成分でエリアジングが発生するため、信号が7.2%歪むことが予想されます。